许多类在使用配置对象创建(实例化)类时都有快捷名称。快捷名称被称为 alias(如果类扩展了 Ext.Component,则为 xtype)。别名/xtype 列在适用类的类名旁边,以供快速参考。
框架类或其成员可以指定为 private 或 protected。否则,类/成员为 public。Public、protected 和 private 是访问描述符,用于传达类或类成员应该如何以及何时使用。
Public 类和类成员可供任何其他类或应用程序代码使用,并且可以作为主要产品版本中的稳定和持久内容依赖。公共类和成员可以通过子类安全地扩展。
Protected 类成员是稳定的 public 成员,旨在由拥有类或其子类使用。受保护的成员可以通过子类安全地扩展。
Private 类和类成员在框架内部使用,不 предназначен для использования разработчиками приложений. 应用程序开发人员不应使用私有类和成员。私有类和成员可能随时更改或从框架中省略,恕不另行通知,不应在应用程序逻辑中依赖它们。
static 标签。*请参阅下面的静态。下面是一个示例类成员,我们可以对其进行剖析,以显示类成员的语法(在本例中,从 Ext.button.Button 类查看的 lookupComponent 方法)。
让我们看一下成员行的每个部分
lookupComponent)( item ))Ext.Component)。对于不返回除 undefined 之外的任何内容的方法,可以省略此项,或者可以显示为以正斜杠 / 分隔的多个可能值,表示返回的内容可能取决于方法调用的结果(即,如果 get 方法调用成功,则方法可能返回 Component,如果失败,则返回 false,这将显示为 Ext.Component/Boolean)。PROTECTED - 请参阅下面的标志部分)Ext.container.Container)。如果成员源自当前类,则源类将显示为蓝色链接;如果成员从祖先类或混合类继承,则显示为灰色。view source)item : Object)。undefined 之外的值,“返回值”部分将注释返回的类或对象类型以及描述(示例中为 Ext.Component)Available since 3.4.0 - 示例中未显示),紧接在成员描述之后Defaults to: false)API 文档使用许多标志来进一步传达类成员的功能和意图。标签可以用文本标签、缩写或图标表示。
classInstance.method1().method2().etc();false,则标记为可阻止的事件将不会触发- 表示框架类
- Singleton 框架类。*有关更多信息,请参阅 singleton 标志
- 组件类型框架类(Ext JS 框架中扩展 Ext.Component 的任何类)
- 表示类、成员或指南在当前查看的版本中是新的
- 表示类型为 config 的类成员
- 表示类型为 property 的类成员
- 表示类型为 method 的类成员
- 表示类型为 event 的类成员
- 表示类型为 theme variable 的类成员
- 表示类型为 theme mixin 的类成员
- 表示类、成员或指南在当前查看的版本中是新的
在 API 文档页面的类名正下方是一行按钮,对应于当前类拥有的成员类型。每个按钮显示按类型计数的成员数(此计数在应用过滤器后会更新)。单击按钮会将您导航到该成员部分。将鼠标悬停在成员类型按钮上将显示该类型的所有成员的弹出菜单,以便快速导航。
与类配置选项相关的 Getting 和 setter 方法将显示在方法部分以及 API 文档和成员类型菜单的配置部分中,就在它们所作用的配置下方。getter 和 setter 方法文档将在配置行中找到,以便于参考。
您的页面历史记录保存在本地存储中,并显示在顶部标题栏正下方(使用可用的实际空间)。默认情况下,显示的唯一搜索结果是与您当前查看的产品/版本匹配的页面。您可以通过单击历史记录栏右侧的 按钮并选择“全部”单选按钮来展开显示的内容。这将显示历史记录栏中所有产品/版本的所有最近页面。
在历史记录配置菜单中,您还将看到最近访问页面的列表。结果按“当前产品/版本”和“全部”单选按钮过滤。单击 按钮将清除历史记录栏以及本地存储中保存的历史记录。
如果在历史记录配置菜单中选择“全部”,则将启用“在历史记录栏中显示产品详细信息”复选框选项。选中后,每个历史页面的产品/版本将与历史记录栏中的页面名称一起显示。将光标悬停在历史记录栏中的页面名称上也会将产品/版本显示为工具提示。
可以使用页面顶部的搜索字段搜索 API 文档和指南。
在 API 文档页面上,还有一个过滤器输入字段,该字段使用过滤器字符串过滤成员行。除了按字符串过滤外,您还可以按访问级别、继承和只读过滤类成员。这是通过使用页面顶部的复选框完成的。
API 类导航树底部的复选框过滤类列表以包含或排除私有类。
单击空的搜索字段将显示您最近 10 次搜索,以便快速导航。
每个 API 文档页面(Javascript 原始类型页面除外)都有一个与该类相关的元数据菜单视图。此元数据视图将具有以下一项或多项
Ext.button.Button 类具有 Ext.Button 的备用类名)。备用类名通常是为了向后兼容性而维护的。可运行示例 (Fiddles) 默认在页面上展开。您可以使用代码块左上角的箭头单独折叠和展开示例代码块。您还可以使用页面右上角的切换按钮切换所有示例的折叠状态。切换所有状态将在页面加载之间记住。
类成员默认在页面上折叠。您可以使用成员行左侧的箭头图标或右上角的展开/折叠所有切换按钮全局展开和折叠成员。
在较窄的屏幕或浏览器上查看文档将导致针对较小外形尺寸优化的视图。桌面视图和“移动”视图之间的主要区别在于
可以通过单击 API 文档页面顶部的类名来查看类源代码。可以通过单击成员行右侧的“查看源代码”链接来查看类成员的源代码。
用于声明接受对象并根据关联模板将其转换为 HTML 的方法的标签接口。方法返回 SafeHtml 实例,该实例可在许多 GWT 和 GXT 小部件中用于呈现内容。
XTemplates 使通过各种功能生成内容变得容易。
{property} 和 {path.to.property},它引用给定的对象属性。模板是使用扩展 XTemplate 并包含注释 HTML 源并返回 SafeHtml 的接口创建的。
使用带有注释 HTML 源的 XTemplate 的示例
public interface SampleXTemplates extends XTemplates {
// Annotated HTML source with {name} property
@XTemplate("<div>Hello, {name}!</div>")
SafeHtml hello(String name);
}
然后可以通过在模板类上调用 GWT.create 来创建 XTemplate 实例
private SampleXTemplates tpl = GWT.create(SampleXTemplates.class);
调用 tpl.hello("test") 的示例将返回呈现的注释 HTML 的 SafeHtml 实例。
public void display() {
// Displays Hello, test! and renders HTML as <div>Hello, test!<div>
RootPanel.get().add(new HTML(tpl.hello("test")));
}
存在两种加载 HTML 模板源的方法,内联注释 HTML 或注释外部 HTML 源。
内联注释 HTML 源 和 外部注释 HTML 源 的示例
public interface SampleXTemplates extends XTemplates {
// Inline annotated HTML source
@XTemplate("<div>Hello, {name}!</div>")
SafeHtml hello(String name);
// External annotated HTML source file.
@XTemplate(source = "hello.html")
SafeHtml helloExternal(String name);
}
使用 XTemplate 模板方法的示例
public void display() {
// XTemplate instantiation
SampleXTemplates tpl = GWT.create(SampleXTemplates.class);
// Displays: Hello, Fred! or <div>Hello, Fred!</div>
RootPanel.get().add(new HTML(tpl.hello("Fred")));
// Displays: Hello, Willma! or <div>Hello, Willma!</div>
RootPanel.get().add(new HTML(tpl.helloExternal("Willma")));
}
将值传递到 HTML 源模板使用 XTemplate 方法变量,该变量可以包括字符串、原始类型、对象、迭代对象、嵌套迭代对象和多个方法参数。诸如 {property} 和 {path.to.property} 之类的属性是 HTML 源属性和/或 XTemplate 源中的变量,属性查找规则在使用期间将其替换为属性值。
通过 String 和原始类型将数据传递到模板。
变量通过用花括号包围名称来定义,例如 {property}
public interface SampleXTemplates extends XTemplates {
// Using a String variable
@XTemplate("<div>Hello, {name} are you {age} years old?</div>")
SafeHtml hello(String name, int age);
}
当在 HTML 源中指定属性时,它将使用多种方法在提供的值中查找该属性的值。
在 HTML 源中使用 {name} 属性的示例将使用这些对象访问器来尝试查找值
object.getName()
object.hasName()
object.isName()
object.name()
可以提供对象、多个对象、嵌套对象和迭代对象,当这样做时,属性的路径必须在花括号中明确指定,例如 {property} 或 {path.to.property}。
下面方法签名中使用的 Person 对象的示例
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
}
设置带有方法签名中 Person 对象的 hello(Person person) 方法,然后在 HTML 源中提供 Person 的 {name} 和 {age} 属性。
public interface SampleXTemplates extends XTemplates {
// Providing person instance to the XTemplate method.
@XTemplate("<div>Hello, {name}! Is your age {age}?</div>")
SafeHtml hello(Person person);
}
使用 XTemplate 方法 hello(person) 示例
public void displayTemplates() {
SampleXTemplates tpl = GWT.create(SampleXTemplates.class);
// Displays: Hello, Barney! Is your age 34? or <div>Hello, Barney! Is your age 34?</div>
Person barney = new Person("Barney", 34);
RootPanel.get().add(new HTML(tpl.hello(barney)));
}
在 XTemplate 方法签名中提供多个对象需要在 HTML 源中使用特定路径,例如 {object1.path} 和 {object2.path}。
使用两个对象的示例
public class Person {
private String name;
private List<Person> kids;
public Person(String name, List<Person> kids) {
this.name = name;
this.kids = kids;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public List<Person> getKids() {
return kids;
}
}
public class Book {
private String title;
public Book(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
}
XTemplate 方法中多个对象的示例
public interface SampleXTemplates extends XTemplates {
@XTemplate("<div>Hello, {person.name}! Do you like the book {book.title}?</div>")
SafeHtml hello(Person person, Book book);
}
使用多对象 XTemplate 方法的示例
public void display() {
SampleXTemplates tpl = GWT.create(SampleXTemplates.class);
Person fred = new Person("Fred");
Book book = new Book("Ice Age");
// Display Hello, Fred! Do you like the book Ice Age? or <div>Hello, Fred! Do you like the book Ice Age?</div>
RootPanel.get().add(new HTML(tpl.hello(fred, book)));
}
在 HTML 源中指定嵌套对象属性需要特定的路径属性,例如 {path.to.property}。
带有嵌套 Person,名为 father 的 Person 示例。
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private Person father;
public Person(Person father, String name, int age) {
this.father = father;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public Person getFather() {
return father;
}
}
提供嵌套 person father 的路径的示例,例如 {father.name}
public interface SampleXTemplates extends XTemplates {
// Providing person instance to the XTemplate method.
// {name} uses Person.getName();
// {age} uses Person.getAge();
// {father.name} uses Person.getFather().getName();
@XTemplate("<div>Hello, {name}! Is your age {age}? {name}‘s father is {father.name}.</div>")
SafeHtml hello(Person person);
}
使用 XTemplate 的示例
public void display() {
SampleXTemplates tpl = GWT.create(SampleXTemplates.class);
// Displays: Hello, Barney! Is your age 34?
Person father = new Person(null, "Bob", 61);
Person barney = new Person(father, "Barney", 34);
RootPanel.get().add(new HTML(tpl.hello(barney)));
}
通过指定嵌套对象变量的属性路径,更深入地访问对象图属性。
带有嵌套的 Person 对象图示例。
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private Person father;
private Book favoriteBook;
public Person(Person father, String name, int age, Book favoriteBook) {
this.father = father;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.favoriteBook = favoriteBook;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public Person getFather() {
return father;
}
public Book getFavoriteBook() {
return favoriteBook;
}
}
public class Book {
private String title;
private Recommendation recommendation;
public Book(String title, Recommendation recommendation) {
this.title = title;
this.recommendation = recommendation;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public Recommendation getRecommendation() {
return recommendation;
}
}
public class Recommendation {
private String message;
public Recommendation(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
}
XTemplate HTML 源的示例
<!-- hello.html file -->
<div>
Hello, {name}! Is your age {age}?
{name}‘s father is {father.name}.
My favorite book is {favoriteBook.title} and
has recommendation: {favoriteBook.recommendation.message}
</div>
使用更深层次的嵌套属性引用的示例
public interface SampleXTemplates extends XTemplates {
// Providing person instance to the XTemplate method.
// {name} uses Person.getName();
// {age} uses Person.getAge();
// {father.name} uses Person.getFather().getName();
// {favoriteBook.title} uses Person.getFavoriteBook().getTitle();
// {favoriteBook.recommendation.message} uses Person.getFavoriteBook().getRecommendation().getMessage();
@XTemplate(source = "hello.html")
SafeHtml hello(Person person);
}
使用 XTemplate 的示例
public void display() {
SampleXTemplates tpl = GWT.create(SampleXTemplates.class);
// Displays: Hello, Barney! Is your age 34? Barney's father is Bob. My favorite book is
// Dinosaurs and has recommendation: This book was good.
Recommendation recommendation = new Recommendation("This book was good.");
Book book = new Book("Dinosaurs", recommendation);
Person father = new Person(null, "Bob", 61, null);
Person barney = new Person(father, "Barney", 34, book);
RootPanel.get().add(new HTML(tpl.hello(barney)));
}
内置属性格式化程序存在于货币、日期、小数、数字和科学数据类型的字符串格式化中。
内置字符串格式化程序
{property:currency}
{property:date("format")}
{property:decimal}
{property:number("format")}
{property:scientific}
将属性格式化为货币
{property:currency}
使用 {money:currency} 的示例
// Example of object for use with this example
public class Person {
private String name;
private BigDecimal money;
public Person(String name, BigDecimal money) {
this.name = name;
this.money = money;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public BigDecimal getMoney() {
return money;
}
}
// XTemplate using {money:currency} formatting
public interface SampleXTemplates extends XTemplates {
@XTemplate("<div>You owe me {money:currency}.</div>")
SafeHtml hello(Person person);
}
// Using the XTemplate
public void display() {
SampleXTemplates tpl = GWT.create(SampleXTemplates.class);
// Displays: You owe me US$1.23.
BigDecimal money = new BigDecimal("1.23");
Person barney = new Person("Barney", money);
RootPanel.get().add(new HTML(tpl.hello(barney)));
}
将属性格式化为日期:DateTimeFormat Javadoc - 格式化选项
{property:date}
{property:date("[custom format]")}
{property:date("M/d/y")} // default
{property:date("mm/dd/yyyy")}
使用 {property:date} 的示例
// Example of object for use with this example
public class Person {
private String name;
private Date hangout;
public Person(String name, Date hangout) {
this.name = name;
this.hangout = hangout;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Date getHangout() {
return hangout;
}
}
// XTemplate using {hangout:date} formatting
public interface SampleXTemplates extends XTemplates {
@XTemplate("<div>Hello, {name}! Lets hangout on {hangout:date}.</div>")
SafeHtml hello(Person person);
}
// Using XTemplate
public void display() {
SampleXTemplates tpl = GWT.create(SampleXTemplates.class);
// Displays: Hello, Barney! Lets hangout on 12/31/2014.
Date hangout = new Date(2014-1900, 11, 31);
Person barney = new Person("Barney", hangout);
RootPanel.get().add(new HTML(tpl.hello(barney)));
}
将属性格式化为小数
{property:decimal}
使用 {property:decimal} 的示例
// Example of object for use with this example
public class Person {
private String name;
private double pi;
public Person(String name, double pi) {
this.name = name;
this.pi = pi;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public double getPi() {
return pi;
}
}
// XTemplate using {pi:decimal} formatting
public interface SampleXTemplates extends XTemplates {
@XTemplate("<div>Would you like some apple {pi:decimal}?</div>")
SafeHtml hello(Person person);
}
// Using XTemplate
public void display() {
SampleXTemplates tpl = GWT.create(SampleXTemplates.class);
// Would you like some apple 3.14?
double pi = 3.14;
Person barney = new Person("Barney", pi);
RootPanel.get().add(new HTML(tpl.hello(barney)));
}
将属性格式化为数字:NumberFormat Javadoc - 格式化选项
{property:number}
{property:number("[custom format]")}
{property:number("#")} // default
{property:number("#,##0.00")}
使用 {property:number} 的示例
// Example of object for use with this example
public class Person {
private String name;
private double pie;
public Person(String name, double pie) {
this.name = name;
this.pie = pie;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public double getPie() {
return pie;
}
}
// XTemplate using {pie:number} formatting
public interface SampleXTemplates extends XTemplates {
@XTemplate("<div>Would you like some apple {pie:number(\"#,##0.00\")}?</div>")
SafeHtml hello(Person person);
}
// Using XTemplate
public void onModuleLoad() {
SampleXTemplates tpl = GWT.create(SampleXTemplates.class);
// Would you like some apple 3.14?
double pie = 3.14;
Person barney = new Person("Barney", pie);
RootPanel.get().add(new HTML(tpl.hello(barney)));
}
将属性格式化为科学计数法
{property:scientific}
使用 {pie:scientific} 的示例
// Example of object for use with this example
public class Person {
private String name;
private double pie;
public Person(String name, double pie) {
this.name = name;
this.pie = pie;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public double getPie() {
return pie;
}
}
// XTemplate using {pie:scientific} formatting
public interface SampleXTemplates extends XTemplates {
@XTemplate("<div>Would you like some apple {pie:scientific}?</div>")
SafeHtml hello(Person person);
}
// Using XTemplate
public void display() {
SampleXTemplates tpl = GWT.create(SampleXTemplates.class);
// Would you like some apple 3E0?
double pie = 3.141592653589793238462643383279502884197169399;
Person barney = new Person("Barney", pie);
RootPanel.get().add(new HTML(tpl.hello(barney)));
}
如果内置属性格式化程序无法提供格式化值所需的内容,请构建自定义格式化程序,如下例所示。此自定义格式化程序示例可以将字符串缩短为特定长度。
用于示例的对象的示例
public class Person {
private String name;
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
带有自定义格式化程序的 XTemplate HTML 源示例
<!-- hello.html file -->
<div>
<p>
<!-- applies the custom formatter :shorten(7) -->
Hello {person.name:shorten(7)}!
</p>
</div>
ShortenFactory 实例化的格式化程序的示例
import com.sencha.gxt.core.client.XTemplates.Formatter;
import com.sencha.gxt.core.client.util.Format;
public class Shorten implements Formatter<String> {
private int length;
public Shorten(int length) {
this.length = length;
}
@Override
public String format(String data) {
return Format.ellipse(data, length);
}
}
在 XTemplates 接口中注释的 ShortenFactory 类的示例
public class ShortenFactory {
public static Shorten getFormat(int length) {
return new Shorten(length);
}
}
注释的 shortner 格式化程序的示例
@FormatterFactories(@FormatterFactory(factory = ShortenFactory.class, name = "shorten"))
public interface SampleXTemplates extends XTemplates {
@XTemplate(source = "hello.html")
SafeHtml hello(Person person);
}
使用带有自定义格式化程序的 XTemplate 的示例
public void display() {
SampleXTemplates tpl = GWT.create(SampleXTemplates.class);
// Displays: Hello Barn...!
Person barney = new Person("Barney Rubbel");
RootPanel.get().add(new HTML(tpl.hello(barney)));
}
使用 <tpl for="." /> 标签迭代列表和数组。
<tpl for="." /> 并且提供的属性是迭代对象时,将在标签内进行迭代。<tpl/> 标签内迭代时,特殊变量 {#} 将提供当前数组索引+1 (1,2,3...)。任何类型的嵌套都可以使用属性,尽管必须给出特定路径才能引用属性。
this XTemplate 签名中提供的值。在 <tpl for="." /> 标签中使用嵌套属性引用的示例
<tpl for="." /> // 'this' or kids or the given iterative value
<tpl for="kids" /> // this.getKids();
<tpl for="kids.friends" /> // this.getKids().getFriends();
<tpl for="kids.friends.teachers" /> // this.getKids().getFriends().getTeachers();
使用 <tpl for="." /> 迭代 List<Person> 的示例
// Example object
public class Person {
private String name;
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
HTML 源示例
<!-- hello.html file -->
<div>
<tpl for='.'>
<p>{#}. Hello {name}!</p>
</tpl>
</div>
XTemplate 示例
// Example XTemplate with List<Person> people iteration
public interface SampleXTemplates extends XTemplates {
@XTemplate(source = "hello.html")
SafeHtml hello(List<Person> people);
}
使用示例
// Example of using the XTemplate
public void display() {
SampleXTemplates tpl = GWT.create(SampleXTemplates.class);
List<Person> people = new ArrayList<Person>();
people.add(new Person("Fred"));
people.add(new Person("Barney"));
// Displays:
// 1. Hello Fred!
// 2. Hello Barney!
RootPanel.get().add(new HTML(tpl.hello(people)));
}
使用 kids 的另一个嵌套属性示例,例如 <tpl for="kids" />
// Example object
public class Person {
private String name;
private List<Person> kids;
public Person(String name, List<Person> kids) {
this.name = name;
this.kids = kids;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public List<Person> getKids() {
return kids;
}
}
HTML 源示例
<!-- hello.html -->
<div>
<tpl for='.'>
<p>
{#}. Hello {name}! Kids:
<tpl for='kids'>{name} </tpl>
</p>
</tpl>
</div>
XTemplate 示例
// Example XTemplate with deeper object graph iteration
public interface SampleXTemplates extends XTemplates {
@XTemplate(source = "hello.html")
SafeHtml hello(List<Person> people);
}
使用示例
// Using the XTemplate
public void display() {
SampleXTemplates tpl = GWT.create(SampleXTemplates.class);
List<Person> fredsKids = new ArrayList<Person>();
fredsKids.add(new Person("Pebbles", null));
fredsKids.add(new Person("Stony", null));
List<Person> barneysKids = new ArrayList<Person>();
barneysKids.add(new Person("Bam-Bam", null));
List<Person> people = new ArrayList<Person>();
people.add(new Person("Fred", fredsKids));
people.add(new Person("Barney", barneysKids));
// Displays:
// 1. Hello Fred! Kids: Pebbles Stony
// 2. Hello Barney! Kids: Bam-Bam
RootPanel.get().add(new HTML(tpl.hello(people)));
}
<tpl if="expression" /> 标签提供表达式的条件评估。
else 运算符,但可以使用两个相反的 if 语句。If 语句示例 <tpl if="expression" />
<tpl if="needsIcon" />
<tpl if="id == 'download'" />
<tpl if="name == "Jack"" />
<tpl if="age > 1 && age < 10" />
<tpl if="age >= 10 && age < 18" />
引号封装规则是 XML 标记的规则,相同的规则在此处适用。
单引号值封装可以通过几种方式完成。
// double quote with single quote encapsulation
<tpl if="id == 'download'" />
// escaping single quotes
<tpl if="id == \'download\'" />
可以使用双引号,但必须将它们从 " 编码为 "
// "Jack" is encoded as "Jack"
<tpl if="name == "Jack"" />
XTemplate 系统使用 xml,它需要对这些字符进行编码。
| 编码字符 | |
|---|---|
| 字符 | 编码 |
| " | " |
| > | > |
| < | < |
使用 <tpl if="expression" /> 标签的示例。
HTML 源示例
<!-- hello.html file -->
<div>
<p>
Hello {person.name}! Kids with age > 3:
<tpl for='person.kids'>
<!-- if statement with encoded '>' as > -->
<tpl if="age > 3">
{name}
</tpl>
</tpl>
</p>
</div>
XTemplate 示例
public interface SampleXTemplates extends XTemplates {
@XTemplate(source = "hello.html")
SafeHtml hello(Person person);
}
使用 XTemplate 的示例
public void onModuleLoad() {
SampleXTemplates tpl = GWT.create(SampleXTemplates.class);
List<Person> kids = new ArrayList<Person>();
kids.add(new Person("Pebbles", 7, null));
kids.add(new Person("Stony", 8, null));
kids.add(new Person("Bam-Bam", 2, null));
Person fred = new Person("Fred", 34, kids);
// Displays: Hello Fred! Kids with age > 3: Pebbles Stony
RootPanel.get().add(new HTML(tpl.hello(fred)));
}
基本数学运算符可以直接应用于数值数据值。
| + | - | * | / |
数学表达式必须包含在方括号 {[expression]} 或 {[year+5]} 中
{[expression]}
{[year+5]}
{[price*(quantity+1.23)]}
可以使用基本 Java 类型数学表达式。这种 Java 类型的数学是有限的,更复杂的数学表达式更适合在 bean getter 访问器中使用。
带有数学表达式的 HTML 源示例
<!-- hello.html file -->
<div>
<p>
Hello {person.name}! Kids with age > 3:
<tpl for='person.kids'>
<tpl if="age > 3">
{name} age:{age} math:{[age+3]}
</tpl>
</tpl>
</p>
</div>
XTemplate 示例
public interface SampleXTemplates extends XTemplates {
@XTemplate(source = "hello.html")
SafeHtml hello(Person person);
}
使用示例
public void onModuleLoad() {
SampleXTemplates tpl = GWT.create(SampleXTemplates.class);
List<Person> kids = new ArrayList<Person>();
kids.add(new Person("Pebbles", 7, null));
kids.add(new Person("Stony", 8, null));
kids.add(new Person("Bam-Bam", 2, null));
Person fred = new Person("Fred", 34, kids);
// Displays: Hello Fred! Kids with age > 3: Pebbles age:7 math:10 Stony age:8 math:11
RootPanel.get().add(new HTML(tpl.hello(fred)));
}
在 XTemplate 中混合 GWT I18N 属性。此示例演示了将 Messages 与 XTemplate 一起使用,并且可以使用其他 I18N 模块类型完成相同的技术。
将 Messages 与 XTemplate 结合使用的示例。
XTemplate 中使用的对象的示例
public class Person {
private String name;
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
包含 Messages 翻译属性的本地化消息文件名的示例
# AppMessages file names
AppMessages.properties
AppMessages_ca.properties
AppMessages_cs.properties
AppMessages_da.properties
AppMessages_de.properties
AppMessages_el_GR.properties
AppMessages_es.properties
AppMessages_fr.properties
AppMessages_hu.properties
AppMessages_it.properties
AppMessages_no.properties
AppMessages_pl.properties
AppMessages_pt_BR.properties
AppMessages_pt_PT.properties
AppMessages_pt.properties
AppMessages_ru.properties
AppMessages_sl.properties
AppMessages_ua.properties
AppMessages_zh.properties
# localized property which is put in all of the AppMessages files
hello = Hello
Messages 示例
// The file name must start in the translated property file names
public interface AppMessages extends Messages {
String hello();
}
带有本地化消息 messages.hello 的 XTemplate HTML 源代码示例
<!-- hello.html file -->
<div>
<p>
{messages.hello} {person.name}!
</p>
</div>
XTemplate 方法示例
public interface SampleXTemplates extends XTemplates {
@XTemplate(source = "hello.html")
SafeHtml hello(AppMessages messages, Person person);
}
使用带有消息的 XTemplates 的示例
public void display() {
AppMessages messages = GWT.create(AppMessages.class);
SampleXTemplates tpl = GWT.create(SampleXTemplates.class);
// Displays: Hello Fred!
Person fred = new Person("Fred");
RootPanel.get().add(new HTML(tpl.hello(messages, fred)));
}
向 HTML 模板元素添加样式。此示例演示了如何将 CSS 资源用作 XTemplate 参数。
一些 css 的示例
/* style.css file */
.widget {
border: 1px red solid;
}
应用程序 CSS 资源的示例
import com.google.gwt.resources.client.ClientBundle;
import com.google.gwt.resources.client.CssResource;
public interface AppResources extends ClientBundle {
public interface WidgetCssResource extends CssResource {
String widget();
}
@Source("style.css")
public WidgetCssResource widgetStyles();
}
使用样式设置 XTemplate 模板的示例
<!-- hello.html file -->
<div class="{style.widget}">
<p>
Hello {person.name}!
</p>
</div>
使用 CSS 资源参数设置 Xtemplate 的示例
public interface SampleXTemplates extends XTemplates {
@XTemplate(source = "hello.html")
SafeHtml hello(WidgetCssResource style, Person person);
}
将 XTemplate 与 CSS 资源一起使用的示例。
public void display() {
SampleXTemplates tpl = GWT.create(SampleXTemplates.class);
AppResources appResources = GWT.create(AppResources.class);
appResources.widgetStyles().ensureInjected();
// Displays: <div class="GCQJNTMCAN"><p>Hello Barney!</p></div>
Person barney = new Person("Barney");
RootPanel.get().add(new HTML(tpl.hello(appResources.widgetStyles(), barney)));
}
由于变量引用是字符串,因此会导致一些常见错误,而 GXT 具有良好的调试日志记录功能,可帮助快速诊断问题。
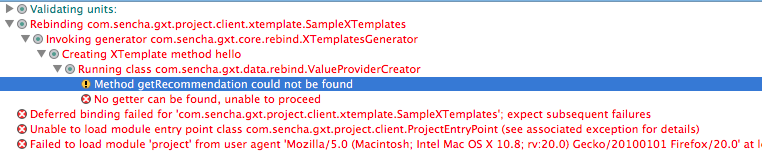
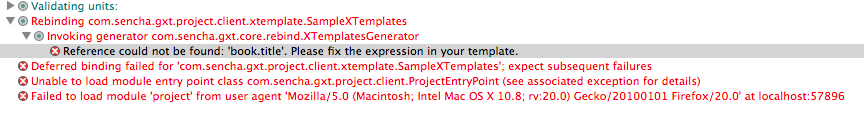
XTemplate 源代码中命名错误的变量将导致构建错误。下面的屏幕截图演示了在 XTemplate 源代码中错误命名变量的错误。该变量被命名为 {book.title},但应该命名为 {favoriteBook.title}。
XTemplates 通过对象的 getter(如 getRecommendation())引用对象实例变量,并且还查找 hasRecomendation()、isRecomendation() 和 recomendation() 来检索实例值。下面的屏幕截图演示了当 getter 或类似方法缺失并给出“no getter”错误时的情况。在此错误中,getRecommendation() 方法缺失,这对应于使用 {favoriteBook.recommendation},它查找 getter 方法 getRecommendation()、hasRecomendation()、isRecomendation() 和 recomendation(),如果它们不存在,则抛出异常 no getter。